
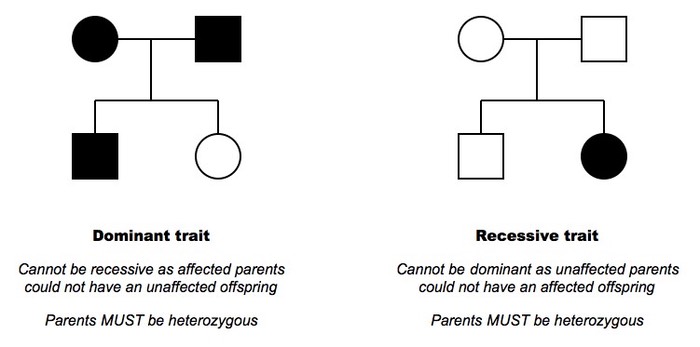
As an inheritance pattern, it is less common than the X-linked recessive type. X-linked dominant inheritance, sometimes referred to as X-linked dominance, is a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosome. JSTOR ( September 2009) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message).Find sources: "X-linked dominant inheritance" – news Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. These include X-linked hypophosphatemia, Focal dermal hypoplasia, Aicardi syndrome, Incontinentia pigmenti, and CHILD.This article needs additional citations for verification. Note: there are very few X-linked dominant disorders. Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (EDA).Other: Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMTX2-3) X-Linked mental retardation: Coffin-Lowry syndrome Įye disorders: Color blindness (red and green, but not blue) Purine-pyrimidine metabolism: Lesch-Nyhan syndrome Danon disease/glycogen storage disease Type IIb.X-linked Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Īndrogen insensitivity syndrome/ Kennedy disease Īmino acid: Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency Ĭarbohydrate metabolism: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.e Sex linkage: X-linked recessive disorders.Vitamin D resistant rickets: X-linked hypophosphatemia.Similarly, individuals with Klinefelter's Syndrome are referred to as "47,XXY Males". Some X-linked dominant conditions such as Aicardi Syndrome are fatal to boys, therefore only girls with these conditions survive. Were this to occur with an X-linked dominant disorder, that daughter would likely experience a more severe form. In such a case, where both parents carry and thus are affected by an X-linked dominant disorder, the chance of a daughter receiving two copies of the X chromosome with the defective gene is 50%, since daughters receive one copy of the X chromosome from both parents. Sons have an equal chance of receiving either of their mother's X chromosomes. Of the sons: 50% will have the disorder, 50% will be completely unaffected.Of their daughters: 100% will have the disorder, since all of the daughters will receive a copy of their father's X chromosome.Their children would inherit the disorder as follows: If both parents were carriers of a defective gene associated with a disease or disorder, they would both have the disorder.
X-linked dominant inheritance works differently depending upon whether the mother (left image) or father (right image) is the carrier of a gene that causes a disease or disorder. Inheritance File:Xlink dominant mother.jpg As a result, X-linked dominant disorders usually show higher expressivity in males than females. Males are normally hemizygous for the X chromosome, having only one copy. The difference between dominant and recessive inheritance patterns also plays a role in determining the chances of a child inheriting an X-linked disorder from their parentage. This is due to the fact that, typically, females have two copies of the X-chromosome, while males have only one copy. Inheritance is determined by the gender of the parent carrying a specific gene and can often seem complex.
In addition, the mother of an affected son is also affected (but not necessarily the other way round).Īs the X chromosome is one of the sex chromosomes (the other being the Y chromosome), X-linked All daughters of an affected father will also be affected but none of his sons will be affected (unless the mother is also affected). The exact pattern of inheritance varies, depending on whether the father or the mother has the trait of interest. X-linked dominant traits do not necessarily affect males more than females (unlike X-linked recessive traits). In medicine, X-linked dominant inheritance indicates that a gene responsible for a genetic disorder is located on the X chromosome, and only one copy of the allele is sufficient to cause the disorder when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
